 Let’s say you see a rogue fighter aircraft on your territory and you want to demolish it. Well, not you per se, but a person who is in charge of these things! Anyway, you send your pilot so that he can chase the aircraft and destroy it. But how will he determine the path of his aircraft so that it takes the shortest path? Bear in mind that the target is moving. If the target moves in a straight line, this is a pretty simple problem. But it almost never happens in real life. Also, if you chase the target but arrive there in a vulnerable position, you might get attacked by the target itself. You need to arrive there in time and also in an offensive position. How do we solve this? Continue reading “The Clairvoyant Curves Of Pursuit”
Let’s say you see a rogue fighter aircraft on your territory and you want to demolish it. Well, not you per se, but a person who is in charge of these things! Anyway, you send your pilot so that he can chase the aircraft and destroy it. But how will he determine the path of his aircraft so that it takes the shortest path? Bear in mind that the target is moving. If the target moves in a straight line, this is a pretty simple problem. But it almost never happens in real life. Also, if you chase the target but arrive there in a vulnerable position, you might get attacked by the target itself. You need to arrive there in time and also in an offensive position. How do we solve this? Continue reading “The Clairvoyant Curves Of Pursuit”
Category: Mathematics
What Do You Know About Infinity?
 What do you think of the term “infinity”? In layman’s terms, infinity is something that has no end, something that is bigger than all the things we know. This is what most people think! Many people who have not seen advanced mathematics do not know about the fact that there are many different types of infinity, some of which are bigger than others. Now how is that possible? Isn’t there just one single infinity which quantifies the essence of uncountability? Continue reading “What Do You Know About Infinity?”
What do you think of the term “infinity”? In layman’s terms, infinity is something that has no end, something that is bigger than all the things we know. This is what most people think! Many people who have not seen advanced mathematics do not know about the fact that there are many different types of infinity, some of which are bigger than others. Now how is that possible? Isn’t there just one single infinity which quantifies the essence of uncountability? Continue reading “What Do You Know About Infinity?”
P vs NP: The Epic Saga
 P vs NP problem is one of the great unsolved problems in theoretical computer science. This problem has become broadly recognized in the mathematical community as a mathematical question because it is fundamental, important and beautiful. It is in fact one of the seven Millennium Prize Problems. If you solve this problem, you get $1 million and become really famous among mathematicians and computer scientists. If you are evil, then you can use your proof to become richer than God, then publish your proof, reject the prize money and become extremely well respected in the mathematics community! Wait a minute, really? How can I use this to become rich? Before we answer that, let’s see what exactly is the difficulty in solving the problem. Shall we? Continue reading “P vs NP: The Epic Saga”
P vs NP problem is one of the great unsolved problems in theoretical computer science. This problem has become broadly recognized in the mathematical community as a mathematical question because it is fundamental, important and beautiful. It is in fact one of the seven Millennium Prize Problems. If you solve this problem, you get $1 million and become really famous among mathematicians and computer scientists. If you are evil, then you can use your proof to become richer than God, then publish your proof, reject the prize money and become extremely well respected in the mathematics community! Wait a minute, really? How can I use this to become rich? Before we answer that, let’s see what exactly is the difficulty in solving the problem. Shall we? Continue reading “P vs NP: The Epic Saga”
Bayesian Classifier
 In machine learning, classification is the process of identifying the category of an unknown input based on the set of categories we already have. A classifier, as the name suggests, classifies things into multiple categories. It is used in various real life situations like face detection, image search, fingerprint recognition, etc. Some of the tasks are really simple and a machine can identify the class with absolute certainty. A common example would be to determine if a given number is even or odd. Pretty simple right! But most of the real life problems are not this simple and there is absolutely no way a machine can identify it with absolute certainty. For example, object recognition, weather prediction, handwriting analysis etc. So how do machines deal with these problems? What approach can be used here? Continue reading “Bayesian Classifier”
In machine learning, classification is the process of identifying the category of an unknown input based on the set of categories we already have. A classifier, as the name suggests, classifies things into multiple categories. It is used in various real life situations like face detection, image search, fingerprint recognition, etc. Some of the tasks are really simple and a machine can identify the class with absolute certainty. A common example would be to determine if a given number is even or odd. Pretty simple right! But most of the real life problems are not this simple and there is absolutely no way a machine can identify it with absolute certainty. For example, object recognition, weather prediction, handwriting analysis etc. So how do machines deal with these problems? What approach can be used here? Continue reading “Bayesian Classifier”
Reimann Hypothesis And Its Connection To Cryptography
 Over the centuries, mathematicians have been involved in solving some of most complex problems. But what is the motivation behind that? The pursuit of truth! But The Clay Mathematics Institute thought that there should be a little more than that. So to celebrate mathematics in the new millennium, they established seven Millennium Prize Problems. The prize money for each problem is one million dollars. That’s pretty exciting! These were some of the most difficult problems over which many mathematicians were racking their brains. Reimann Hypothesis is one of them. The interesting thing about this particular problem is that it has far reaching consequences in the field of modern cryptography and internet security. Now how can an obscure and complex mathematical problem affect cryptography and internet security? Continue reading “Reimann Hypothesis And Its Connection To Cryptography”
Over the centuries, mathematicians have been involved in solving some of most complex problems. But what is the motivation behind that? The pursuit of truth! But The Clay Mathematics Institute thought that there should be a little more than that. So to celebrate mathematics in the new millennium, they established seven Millennium Prize Problems. The prize money for each problem is one million dollars. That’s pretty exciting! These were some of the most difficult problems over which many mathematicians were racking their brains. Reimann Hypothesis is one of them. The interesting thing about this particular problem is that it has far reaching consequences in the field of modern cryptography and internet security. Now how can an obscure and complex mathematical problem affect cryptography and internet security? Continue reading “Reimann Hypothesis And Its Connection To Cryptography”
The Butterfly Effect
 This blog post is a continuation of my previous post on Chaos Theory. Although it is not required for you to read that post to understand this post, it would be better if you glance through it once. All of us have heard about the Butterfly Effect. It is one of the very famous examples given in the field of chaos theory. I should also give credit to the movie “The Butterfly Effect” for popularizing this term. So what exactly is butterfly effect? Is it just a theory? Where does it happen in real life? Continue reading “The Butterfly Effect”
This blog post is a continuation of my previous post on Chaos Theory. Although it is not required for you to read that post to understand this post, it would be better if you glance through it once. All of us have heard about the Butterfly Effect. It is one of the very famous examples given in the field of chaos theory. I should also give credit to the movie “The Butterfly Effect” for popularizing this term. So what exactly is butterfly effect? Is it just a theory? Where does it happen in real life? Continue reading “The Butterfly Effect”
Chaos Theory
 Chaos Theory is a mathematical sub-discipline that attempts to explain the fact that complex and unpredictable results can and will occur in systems that are sensitive to their initial conditions. Some common examples of systems that chaos theory helped understand are earth’s weather system, the behavior of water boiling on a stove, migratory patterns of birds, or the spread of vegetation across a continent. The Butterfly Effect is one of more famous examples of chaos theory. I have discussed more about it here. Chaos occurs in nature and it manifests itself in various forms. Chaos-based graphics show up all the time, wherever flocks of little space ships sweep across the movie screen in highly complex ways, or whenever amazing landscapes are displayed in some dramatic movie scene. It is used a lot in movies to generate obscure background using computer-generated chaos art. So what exactly is chaos? How does it work? Continue reading “Chaos Theory”
Chaos Theory is a mathematical sub-discipline that attempts to explain the fact that complex and unpredictable results can and will occur in systems that are sensitive to their initial conditions. Some common examples of systems that chaos theory helped understand are earth’s weather system, the behavior of water boiling on a stove, migratory patterns of birds, or the spread of vegetation across a continent. The Butterfly Effect is one of more famous examples of chaos theory. I have discussed more about it here. Chaos occurs in nature and it manifests itself in various forms. Chaos-based graphics show up all the time, wherever flocks of little space ships sweep across the movie screen in highly complex ways, or whenever amazing landscapes are displayed in some dramatic movie scene. It is used a lot in movies to generate obscure background using computer-generated chaos art. So what exactly is chaos? How does it work? Continue reading “Chaos Theory”
Dynamic Programming
 Most of the techies have come across this concept one time or the other. People know that it’s really good and very useful, but not a lot of them know how exactly it works and why it works in the first place! Let’s say you are presented with a big box of precious stones with different sizes and weights. You have a bag with you which can only hold a limited weight. So obviously you can’t take everything. In particular, you’re constrained to take only what your bag can hold. Let’s say it can only hold W pounds. You also know the market value for each of those stones. Given that you can only carry W pounds, what stones should you pick in order to maximize your profit? Continue reading “Dynamic Programming”
Most of the techies have come across this concept one time or the other. People know that it’s really good and very useful, but not a lot of them know how exactly it works and why it works in the first place! Let’s say you are presented with a big box of precious stones with different sizes and weights. You have a bag with you which can only hold a limited weight. So obviously you can’t take everything. In particular, you’re constrained to take only what your bag can hold. Let’s say it can only hold W pounds. You also know the market value for each of those stones. Given that you can only carry W pounds, what stones should you pick in order to maximize your profit? Continue reading “Dynamic Programming”
Constrained Optimization
 Whenever we think of a real life problem, we always want to get the most optimal result. I said optimal and not the best possible because we don’t have unlimited resources. Given unlimited resources, we would always pick the best one and we don’t have to think about it at all. But unfortunately in real life, this is almost never the case. Let’s say you want to buy a car. Ideally you want the best possible car, but you don’t have unlimited money. So you would buy a car with maximum features while minimizing your cost. This is not so hard to do because you have a limited number of variables. Hence you would just do it manually. What would you do when you have to deal with a lot of variables? How would you do it? Continue reading “Constrained Optimization”
Whenever we think of a real life problem, we always want to get the most optimal result. I said optimal and not the best possible because we don’t have unlimited resources. Given unlimited resources, we would always pick the best one and we don’t have to think about it at all. But unfortunately in real life, this is almost never the case. Let’s say you want to buy a car. Ideally you want the best possible car, but you don’t have unlimited money. So you would buy a car with maximum features while minimizing your cost. This is not so hard to do because you have a limited number of variables. Hence you would just do it manually. What would you do when you have to deal with a lot of variables? How would you do it? Continue reading “Constrained Optimization”
Principal Component Analysis
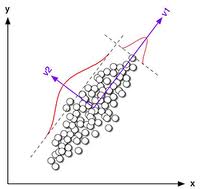 Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is one of most useful tools in the field of pattern recognition. Let’s say you are making a list of people and collecting information about their physical attributes. Some of the more common attributes include height, weight, chest, waist and biceps. If you store 5 attributes per person, it is equivalent to storing a 5-dimensional feature vector. If you generalize it for ‘n’ different attributes, you are constructing an n-dimensional feature vector. Now you may want to analyze this data and cluster people into different categories based on these attributes. PCA comes into picture when have a set of datapoints which are multidimensional feature vectors and the dimensionality is high. If you want to analyze the patterns in our earlier example, it’s quite simple because it’s just a 5-dimensional feature vector. In real-life systems, the dimensionality is really high (often in hundreds or thousands) and it becomes very complex and time-consuming to analyze such data. What should we do now? Continue reading “Principal Component Analysis”
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is one of most useful tools in the field of pattern recognition. Let’s say you are making a list of people and collecting information about their physical attributes. Some of the more common attributes include height, weight, chest, waist and biceps. If you store 5 attributes per person, it is equivalent to storing a 5-dimensional feature vector. If you generalize it for ‘n’ different attributes, you are constructing an n-dimensional feature vector. Now you may want to analyze this data and cluster people into different categories based on these attributes. PCA comes into picture when have a set of datapoints which are multidimensional feature vectors and the dimensionality is high. If you want to analyze the patterns in our earlier example, it’s quite simple because it’s just a 5-dimensional feature vector. In real-life systems, the dimensionality is really high (often in hundreds or thousands) and it becomes very complex and time-consuming to analyze such data. What should we do now? Continue reading “Principal Component Analysis”